Knative是一个开源的企业级解决方案,用于在kubernetes平台中
构建Serveless 和管理事件驱动的应用程序。
介绍
Knative is an Open-Source Enterprise-level solution to build Serverless and Event Driven ApplicationsServerless Containers in Kubernetes environments.- knative 是 k8s 原生扩展组件,用于部署、运行和管理 Serverless 类型的云原生应用
- knative(读音
kay-nay-tiv),由 Google 在 2018 年 7 月正式发布,当前由 Redhat、Google 和 IBM,以及各种初创公司组成的开源社区共同维护
为什么需要 Serverless 容器
- 配置简单,通过简化的 YAML 定义自定义的 CRDs
- 弹性伸缩:支持缩资源数量为 0
- 渐进式发布:根据您的需要选择发布策略
- 事件集成:支持处理来自多个源的事件
- 处理事件:支持事件代理(event broker)触发程序
- 可扩展:Kubernetes 原生集成和扩展
核心组件

说明:
Serving和Eventing协同工作,管理任务和应用Serving- 支持由请求驱动计算
- 关注应用的网络、弹性伸缩(支持缩容至 0)和版本(revision)记录
- When you build or run a function, an Open Container Initiative (OCI) format container image is generated automatically for you, and is stored in a container registry(参考)
- 部署、管理和伸缩无状态应用规模
- 替代 kubernetes Deployment 控制器,负责编排运行基于 HTTP 协议的无状态应用
- knative 的 Serving 对象,相当于 Kubernetes 的 Service + Deployment 的功能
- 流量切分
- 通过在 Pod 扩展时缓冲请求来削峰填谷
- 基于单个请求进行负载均衡
- 基于请求的速度、自动扩缩容
Eventing- 以声明的方式创建对事件源的订阅,并将事件路由到目标端点
- 管理事件的
订阅(subscription)、分发(delivery)和处理 - 基于
pub/sub模型连接Serving
- 旧版本存在的
Build组件,已经拆分为Tekton项目,主要作用包括- 从源码构建出应用镜像
- https://github.com/knative/specs
Knative Serving
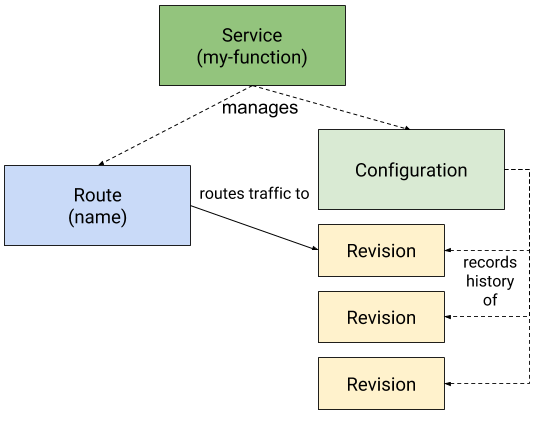
参考:knative Serving,代码入口参考,相关文档
- 相关资源定义在
serving.knative.dev群组中 - 主要包括 4 个 CRDs
Service:service.serving.knative.dev- 自动控制下面三种类型资源对象的管理
- 是对 Serverless 类型应用功能的抽象,负责整个 Serverless 的声明周期
Route:route.serving.knative.dev- 将请求路由到目标
Revision - 支持将流量按比例切分并路由到多个
Revision
- 将请求路由到目标
Configuration:configuration.serving.knative.dev- 定义 Service 期望状态(spec)的配置
- Service 的更新,也将导致 Configuration 的更新
Revision:revision.serving.knative.dev,参考,代码定义- Service 的每次代码或配置变更都生成一个 revision
- revision 是快照数据,不可变
- 相关 metrics,如 kn.queueproxy.depth
- Serving API
Knative Serving 子组件
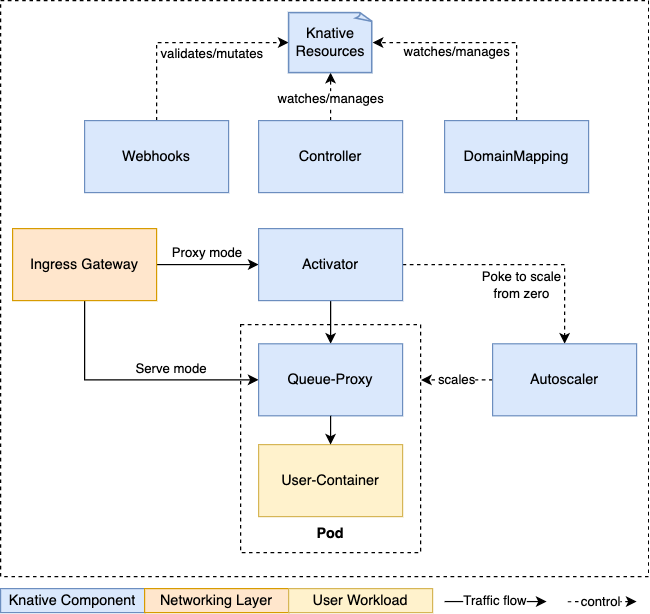
参考:
子组件:
ActivatorRevision 中的 Pod 数量收缩至 0 时,activator 负责接收并缓存相关的请求,同时报告指标数据给 Autoscaler,并在 Autoscaler 在 Revision 上扩展出必要的 Pod 后,再将请求路由至相应的 Revision。AutoscalerKnative 通过注入一个称为 queue-proxy 容器的 sidecar 代理来了解它部署的 Pod 上的请求,而 Autoscaler 会为每个服务使用“每秒请求数”来自动缩放其 Revision 上的 Pod。Controller负责监视 Serving CRD(KService、Configuration、Route 和 Revision)相关的 API 对象并管理它们的生命周期,是 Serving 声明式 API 的关键保障。Webhooks为 Kubernetes 提供的外置 Admission Controller,兼具 Validation 和 Mutation 的功能,主要作用于 Serving 专有的几个 API 资源类型之上,以及相关的 ConfigMap 资源上。负责验证和改变 Knative 资源。DomainMapping将指定的域名映射至 Service、KService,甚至是 Knative Route 之上,从而使用自定义域名访问特定的服务。Queue-Proxy是 Knative Service Pod 中的一个 sidecar 容器。它负责收集指标并在将请求转发到用户容器时强制执行所需的并发性。如果需要的话,它也可以充当队列,类似于 activator
Activator
本质上以通过 golang httputil.ReverseProxy 包实现对流量的代理,核心代理如下:
- activator.main 主函数
- activatorhandler.New activation handler chain
// Create activation handler chain
// Note: innermost handlers are specified first, ie. the last handler in the chain will be executed first
ah := activatorhandler.New(ctx, throttler, transport, networkConfig.EnableMeshPodAddressability, logger, tlsEnabled, tp)
ah = handler.NewTimeoutHandler(ah, "activator request timeout", func(r *http.Request) (time.Duration, time.Duration, time.Duration) { // 设置 timeout
if rev := activatorhandler.RevisionFrom(r.Context()); rev != nil { // 获取对应的 reversion 信息
responseStartTimeout := 0 * time.Second
# ResponseStartTimeoutSeconds 是请求路由层等待容器处理请求并开始发送网络流量的最长秒数。简言之,它衡量的是从请求送达容器到容器开始响应的这段时间。
if rev.Spec.ResponseStartTimeoutSeconds != nil {
responseStartTimeout = time.Duration(*rev.Spec.ResponseStartTimeoutSeconds) * time.Second
}
idleTimeout := 0 * time.Second
if rev.Spec.IdleTimeoutSeconds != nil {
idleTimeout = time.Duration(*rev.Spec.IdleTimeoutSeconds) * time.Second
}
return time.Duration(*rev.Spec.TimeoutSeconds) * time.Second, responseStartTimeout, idleTimeout
}- mainHandler
- var composedHandler http.Handler = httpProxy Create queue handler chain
- activationHandler 在处理请求前,activationHandler 会等待某个修订版本的活动端点 (active endpoint)可用
- ServeHTTP 实现 golang http.ServeHTTP 接口
- a.proxyRequest(revID, w, r.WithContext(proxyCtx), dest, a.usePassthroughLb, isClusterIP) 将请求代理到对应的 revID 和 dest(pod ip)
- proxyRequest
- r.Header.Set(netheader.ProxyKey, activator.Name) 配置 ProxyKey 为当前的 activator.Name
- proxy = pkghttp.NewHeaderPruningReverseProxy(target, hostOverride, activator.RevisionHeaders, false /_ use HTTPS _/)
- NewHeaderPruningReverseProxy 返回一个 httputil.ReverseProxy 实例。这个实例会代理对给定 targetHost 的请求,但在代理之前会移除 headersToRemove 中指定的请求头。如果 hostOverride 不是空字符串,则传出请求的 Host 请求头会被这个显式值替换,同时还会设置 passthrough 负载均衡请求头,以启用 pod 可寻址性。
- ProxyHandler 将请求发送给 next 处理程序,其速率由传入的 breaker 控制,同时将统计数据记录到 stats
- activationHandler 重要成员 Throttler(限流器)是 Knative Serving 自动扩缩容(Autoscaling)机制的一部分,它的主要作用是在服务从零实例(pod)扩容时,管理和限制进入的请求
- Throttler 的核心职责是在服务从 0 扩容时,保护服务不受突发流量的冲击,确保请求能够平稳、可靠地被处理
- Try 方法 proxy the user request
- Try 代码实现
- if err := a.throttler.Try(tryContext, revID, func(dest string, isClusterIP bool) error 是探测业务容器是否可用的重要实现
- 代理到对应的 revID 和 dest(pod ip)
- try 中 rt.breaker.Maybe
- throttler.getOrCreateRevisionThrottler 创建或获取 revisionThrottler
- revisionThrottler 重要成员包括
- lbPolicy
- breaker 核心作用是实现精确的并发控制和请求排队,从而保障用户服务的稳定性和可靠性。它作为流量进入用户容器前的最后一道关卡,扮演着“流量调度员”和“服务守护者”的双重角色。
- breaker.Maybe 函数会根据 Breaker 的并发和队列参数来有条件地执行 thunk。如果并发限制和队列容量已满,Maybe 会不调用 thunk 并立即返回。如果 thunk 得以执行,Maybe 返回 nil,否则返回一个错误。
- if err := b.sem.acquire(ctx) Wait for capacity in the active queue,实现精确的并发控制
- breaker.Maybe 函数会根据 Breaker 的并发和队列参数来有条件地执行 thunk。如果并发限制和队列容量已满,Maybe 会不调用 thunk 并立即返回。如果 thunk 得以执行,Maybe 返回 nil,否则返回一个错误。
- assignedTrackers
- 参数:breakerQueueDepth = 10000 队列中断路器在发送 503 错误之前,可以处理的请求数量。该值必须根据实际生产需求进行调整。这个值同时用于 revisionThrottler(对整个修订版本进行限流)中的断路器和单个 podTracker 断路器。
- rt.numActivators.Store(newNA)
- revisionThrottler 重要成员包括
- Throttler 的核心职责是在服务从 0 扩容时,保护服务不受突发流量的冲击,确保请求能够平稳、可靠地被处理
- ServeHTTP 实现 golang http.ServeHTTP 接口
- infiniteBreaker
- Maybe capacity 可用时执行 thunk
- 多个 activator 和后端 pod 的流量切分,pod 根据 ip 排序,每个 activator 将流量代理到指定的一组后端 pod 上,相关实现参考
- assignSlice 函数的作用是为特定的 Activator 实例挑选一部分 pod 来处理请求。这个机制只在直接通过 pod 的 IP 地址进行路由时才起作用,如果使用 ClusterIP 这种服务抽象,它就没有意义了。此外,为了正确执行,assignSlice 必须接收一份按地址排序的 pod 追踪器列表。
- pickIndices picks the indices for the slicing
- podTracker、NewBreaker podTracker 主要跟踪和管理服务 Pod 的生命周期,并确保请求能够被正确路由到这些 Pod 上
- inferIndex 返回此激活器(activator)切片的索引。如果 inferIndex 返回 -1,则意味着这个激活器暂时还不会接收任何流量,因此不参与切片;这种情况发生在启动后,但在它被接入(threaded into)端点(endpoints)之前(此操作在报告健康状态后最多需要 10 秒)。目前,我们只是对所有激活器的 IP 地址进行排序,并在这个列表中找到自身的索引。
- newRevisionThrottler 中根据 containerConcurrency 使用不同的 lbproxy:
If the number of pods is not divisible by the number of activators, we allocate one pod to each activator exclusively.
examples
1. we have 20 pods and 3 activators -> we'd get 2 remnants so activator with index 0,1 would each pick up a unique tracker
2. we have 24 pods and 5 activators -> we'd get 4 remnants so the activator 0,1,2,3 would each pick up a unique tracker-
一些其他代码
- NewConcurrencyReporter 会创建一个并发报告器(ConcurrencyReporter),这个报告器会监听 reqCh 通道上进入的请求事件(ReqEvents),在 reportCh 通道上收到“滴答”信号时,将统计数据报告给 statCh 通道。
- terminationGracePeriodSeconds
- 代理过程中的一些 header keys
- MakeSKS makes an SKS resource from the PA and operation mode
- https://github.com/knative-extensions/monitoring
-
revisionWatcher.run 周期检查 pod 的状态
-
其他
- 访问
/metrics可以获取各个 ksvc 的排队等情况
- 访问
Autoscaling
Queue-Proxy
Knative Serving 中的 queue-proxy(队列代理)主要负责以下功能:
- 并发请求处理与限流 它会测量自动扩缩器所需的并发请求数量,尤其是在请求路径中移除了激活器(activator)时。此外,如果用户有要求,它还会实施
containerConcurrency(容器并发)的硬性限制。 - 优雅停机
queue-proxy在 Pod 终止时负责处理优雅停机。它的做法是:拒绝新的请求、使就绪检查(readiness checks)失败,但同时继续处理并完成现有请求。 - 性能监控与启动优化
- 报告指标:它会从用户容器的外部报告 HTTP 指标和跟踪信息,这样就可以测量出基础设施所贡献的延迟。
- 加速启动:在启动阶段(即就绪之前),它会更频繁地探测用户容器,以实现比 Kubelet 探测(每秒最多探测一次)更早地提供服务。
- 就绪检查的重写 为了支持上述功能,Knative Serving 会将用户容器的
readinessProbe重写为queue-proxy的一个参数。最终,queue-proxy的就绪检查会同时包含它自身的就绪状态和用户容器的就绪状态。
Knative serving 服务创建的每个 Pod 都会创建一个queue-proxy Sidecar,以强制执行请求并发限制。队列代理预留 25 milliCPU,但不预留内存。队列代理的耗用情况取决于队列中的请求数量以及请求的大小;它可以占用的 CPU 和内存资源没有限制。
请求时,不会缓存请求体,而是业务容器接收到请求时,请求体以客户端指定的 chunk 流过queue-proxy,响应时有 buffer cache,本质上是 httputil.BufferPool。
监听的端口(参考):
// BackendHTTPPort is the backend, i.e. `targetPort` that we setup for HTTP/1 services.
BackendHTTPPort = 8012
// BackendHTTP2Port is the backend, i.e. `targetPort` that we setup for HTTP/2 services.
BackendHTTP2Port = 8013
// BackendHTTPSPort is the backend. i.e. `targetPort` that we setup for HTTPS services.
BackendHTTPSPort = 8112
// QueueAdminPort specifies the port number for
// health check and lifecycle hooks for queue-proxy.
QueueAdminPort = 8022
// AutoscalingQueueMetricsPort specifies the port number for metrics emitted
// by queue-proxy for autoscaler.
AutoscalingQueueMetricsPort = 9090
// UserQueueMetricsPort specifies the port number for metrics emitted
// by queue-proxy for end user.
UserQueueMetricsPort = 9091| Probe Request Source | Path | Extra features | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activator probe requests | :8012 | With header K-Network-Probe=queue. Expected queue as response body. |
Probe requests from Activator before it proxies external requests |
| VirtualService/Gateway probe requests | :8012 | With header K-Network-Probe=probe and non-empty K-Network-Hash header | This is used to detect which version of a VirtualService an Envoy Pod is currently serving. They are proxied from VirtualService to activator/queue-proxy. |
| Kubelet probe requests | :8012 | With non-empty K-Kubelet-Probe header or with header user-agent=kube-probe/* |
I don’t think currently kubectl sends probe requests to this path. We can delete it. Correct me if I was wrong. |
| Queue-proxy Readiness Exec probe requests | :8022/health | Probe requests triggered by Kubelet Readiness Exec probe. |
参考:
- Merge 8022/health to 8012/8013
- Consolidate queue-proxy probe handlers
- queue-proxy 最大队列
- requestAppMetricsHandler query-proxy metrics 指标
Knative Eventing
Knative Eventing 是一个 API 集合,允许应用使用事件驱动架构(Event-driven architecture)模型
核心概念
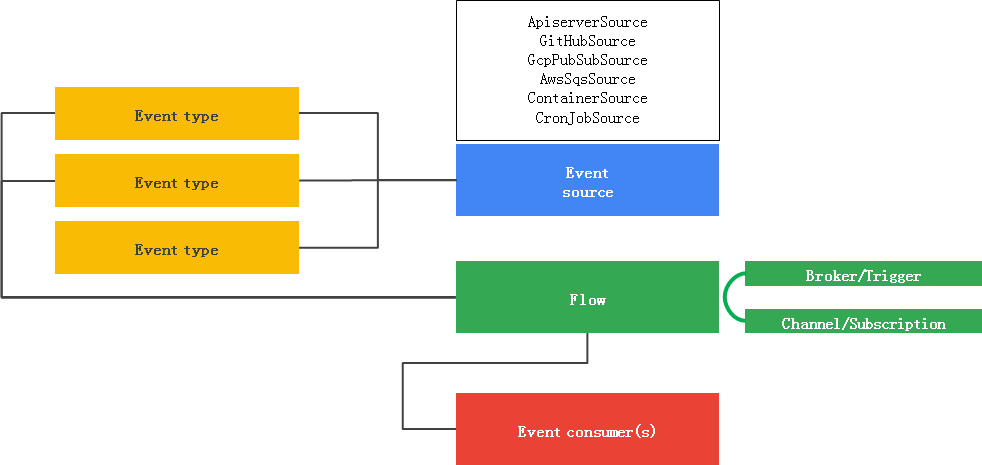
图参考自互联网
事件源(Event Source)事件生产者的抽象,参考事件类型(Event Type)事件类型,在 Event Registry 中定义事件处理流(Eventing Flows)支持两种类型:- Sequence
- Parallel
Event Sinks能接收 Event 的可寻址(addressable)或可调用(Callable)的资源,Knative Eventing Sink 支持三种类型:- Knative Service
- Channels
- Brokers
- Knative Eventing 支持的事件传递模式
- Sources to Sink:
- 单一 Sink 模式,事件接收过程中不存在队列和过滤等操作
- Channels and Subscriptions
- Event Source 将事件发到多个 Channel
- Channel 可以有多个 Subscription(即 Sink)
- Channel 中的事件以 Cloud Event 格式传递
- 不支持事件过滤
- Sources to Sink:
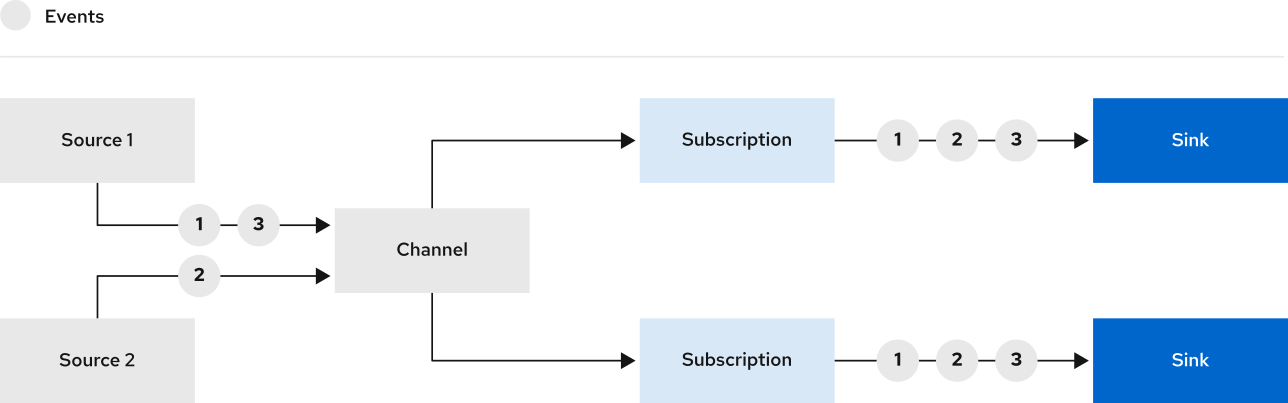
- Brokers and 【
- Brokers and Triggers
- 功能类似于 Channels and Subscriptions 模式,且支持消息过滤
- 事件过滤机制运行 Subscription 使用事件属性的条件表达式(Trigger)筛选事件
- Trigger 负责订阅 Broker,并对 Broker 传递的消息进行过滤,并对消息进行格式化
- 该模式为生产推荐的使用模式
代码架构
Knative 遵循 kubernetes 扩展方式,通过自定义 API 资源类型实现如下:
Serving自动化完成服务的部署和扩缩容Eventing标准化事件驱动- knative
- Serving
- Serving Controller
- Resources API
- Service
- Route
- Configuration
- Revision
- Eventing
- Eventing Controller
- Resources API
- Broker
- Trigger
- EventType
- Serving
重要配置:
- Accessing request traces
- configmap for observability tracing-endpoint
说明
- Knative 并不提供 FaaS 方案,用户可以在 Knative + Kubernetes 基础上,借助其他项目(如 Kyma)构建 FaaS 系统
参考
- https://knative.dev/docs/
- https://github.com/knative/serving/blob/v0.46.1/docs/resources-overview.md
- https://istio.io/latest/zh/blog/2022/merbridge/
- https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/knative-cookbook/9781492061182/ch04.html
最近更新
最新评论